Mosquito control is a perennial topic on the Flatbush Family Network, one of the numerous email discussion groups which cover the different neighborhoods of Brooklyn. Bat houses invariably come up as a way of attracting a natural predator to keep mosquito populations in check. Here I’m reprising and updating my posts on these and related topics from last year.
White-Nose Syndrome (WNS)
Last Spring I wrote about White-Nose Syndrome (WNS). A breakthrough that occurred just in the past few months is that the “White-Nose” has been identified as a group of previously unknown species of Geomyces fungus. It’s still unknown whether it’s a symptom – such as an opportunistic infection – or a cause or contributor.
Bats exhibiting white-nose syndrome in Hailes Cave, Albany County, NY, one of the first caves in which WNS was observed. Photo: Nancy Heaslip, NYS DEC.

Bob Hoke of the District of Columbia Grotto (DCG) of the National Speleological Society (NSS) maintains an excellent chronology of WNS news and understanding. WNS has already killed hundreds of thousands of bats across the northeast over the past four winters. Mortality has been as high as 90% in some caves. It’s estimated that 75% of northeastern bats have died in just four years. Unfortunately, it continues to spread; for the first time, it’s also been found or suspected in New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylania, Virginia and West Virginia.
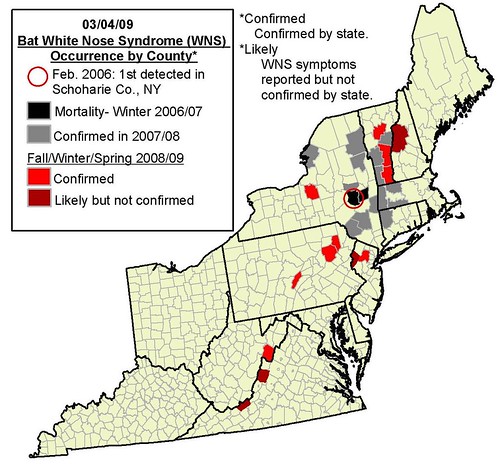
Map of occurrence of White Nose Syndrome by county as of March 4, 2009. WNS was later confirmed in Virginia. Credit: courtesy of Cal Butchkoski, Pennsylvania Game Commission
Because of the high mortality, rapid spread, and still-unknown causes of the disease, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (US FWS) has issued a cave advisory to suspend all caving activities in affected states, and take precautions in states where WNS has not yet been detected:
The evidence collected to date indicates that human activity in caves and mines may be assisting the spread of WNS. Therefore, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is recommending actions to reduce the risks of further spread of WNS:
- A voluntary moratorium on caving in states with confirmed WNS and all adjoining states;
- Nationally, in states not WNS-affected or adjoining states, use clothing and gear that has never been in caves in WNS-affected or adjoining states;
- State and federal conservation agencies should evaluate scientific activities for their potential to spread WNS; and
- Nationally, researchers should use clothing and gear that has never been in caves in a WNS-affected or adjoining state.
This also applies to mines used by cavers.
These recommendations will remain in effect until the mechanisms behind transmission of WNS are understood, and/or the means to mitigate the risk of human-assisted transport are developed.
There was a big thing that came out in the environmental reports last year that chemical mosquito killers are quite bad for the environment and killed more than just mosquitoes. They might even be part of the reason why there is a bacteria/virus killing off northeastern bats. Although, scientists haven’t found anything conclusive it seems.
– via Flatbush Family Network
WNS research is ongoing, but it’s still not known what the cause is. A plausible explanation is immunodeficiency caused by environmental contamination, such as insecticides sprayed for West Nile Virus, but again, that’s just one of several hypotheses being explored by researchers. A pathogen such as a virus, bacteria or fungus is likely due to the patterns by which it’s spreading.
Bat Houses
Bat houses seem like a great idea. At night, bats eat about 1,000 pesky insects an hour. I don’t know how one attracts bats to your bat house but I’ve seen them in the evening in Prospect Park, amazing little creatures that they are.
– via Flatbush Family Network
I wrote about bat houses last year. Bats have specific requirements for roosting sites. Most of the houses I’ve seen commercially available are too small or lacking in other requirements. The National Wildlife Federation (NWF) article, “Why I Built a Bat House,” contains detailed instructions for building a house that meets current knowledge about bats roosting needs.
The bat house I purchased last year from Bat Conservation International before I installed it on the side of the second floor porch – my “tree fort” – at the back of my house.

Note that this is the time of year when bats are looking for their “summer homes.” I put mine up mid-April last year, which was a little late. I’m hoping they find it and set up house this year!
General information about bats
Is there ANY danger to my 4 year old son? Do bats poop/pee/spit anything bad for him? Do they really only come out at night?
– via Flatbush Family Network
Bats really do only come out at night. You’re most likely to see them at dusk, when they leave their roosts, and dawn, when they return. At the end of last summer, I saw a few on my block flying amidst the gaps between the canopies of the street trees. They seemed to be feasting on the insects attracted to the street lights.
Many people are concerned about rabies. While sensible caution is warranted, the risk is extremely low. In New York City, you’re more likely to contract West Nile Virus (WNV), which bats help combat by eating mosquitoes which carry the virus. If you see any normally nocturnal animal – such as a bat, raccoon or opossum – out in the open during the day, keep children and pets away from it and notify animal control by calling 311.
[bit.ly]
[TinyURL]
Related Content
Rabies in NYC: Facts and Figures, 2008-07-08
Bat Houses, 2008-04-13
Northeastern Bats in Peril, 2008-03-18
Other posts about bats
Links
Bats
Bats of New York, Eileen Stegemann and Al Hicks, Conservationist, February 2008, NYSDEC
Bat Conservation International (BCI)
Bat Houses
Why I Built a Bat House, Carla Brown, National Wildlife Federation (NWF) (H/T Sara S. via Flatbush Family Network)
Bats Wanted, Al Hicks and Eileen Stegemann, Conservationist, February 2008, NYSDEC
The importance of bat houses, Organization for Bat Conservation
The Bat House Forum
White-Nose Syndrome
An excellent chronology of WNS is maintained by Bob Hoke of the District of Columbia Grotto (DCG) of the National Speleological Society (NSS).
White-Nose Syndrome Confirmed in VA Bats, WHSV, Richmond, VA, 2009-04-02
Cave activity discouraged to help protect bats from deadly white-nose syndrome, Press Release, U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service, 2009-03-26
Fungus Kills About 90 Percent Of Connecticut’s Bats, Rinker Buck, Hartford Courant, 2009-03-18 (H/T NewYorkology via Twitter)
Newly Identified Fungus Implicated in White-Nose Syndrome in Bats, Press Release, U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), 2008-10-31
Bats dying off across western Maine, Maine Sun Journal, 2008-07-19 (H/T Center for Biological Diversity)
Dying Bats in the Northeast Remain a Mystery, USGS Newsroom, 2008-05-09
First It Was Bees, Now It’s Bats That Are Dying, Natural News, 2008-04-11
Bats in the Region Are Dying From a Mysterious Ailment, Litchfield County Times, 2008-04-03
Bats Perish, and No One Knows Why, New York Times Science Section, 2008-03-25
Bat Die-Off Prompts Investigation, Environment DEC, March 2008, NYSDEC
White-nose Syndrome Threatens New York’s Bats, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (NYSDEC)
White-Nose Syndrome, Pennsylvania Game Commission (PGC)
White-Nose Syndrome in bats: Something is killing our bats, U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service, Northeast Region
Mystery Disease Kills U.S. Bats, Bat Conservation International
Bat Crisis: The White-Nose Syndrome, Center for Biological Diversity
White Nose Syndrome Page, Liaison on White Nose Syndrome, National Speleological Society (NSS)
Something is killing our bats: The white-nose syndrome mystery, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Wikipedia: White-nose syndrome














